An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a normal body part. There are at least 80 types of autoimmune diseases. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms include low grade fever and feeling tired. Often symptoms come and go.
The cause is generally unknown. Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus run in families, and certain cases may be triggered by infections or other environmental factors. Some common diseases that are generally considered autoimmune include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, Graves’ disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis can be difficult to determine.
While treatment usually improves symptoms they do not typically cure the disease. About 24 million (7%) people in the United States are affected by an autoimmune disease.Women are more commonly affected than men. Often they start during adulthood. The first autoimmune diseases were described in the early 1900s.
Your immune system helps protect you from bacteria and other invaders, but a poor immune function also impacts on many other body systems from the nervous system to hormones. Pinpointing immune issues can be challenging, as immune issues can present in many ways and any one symptom or even all of them can be linked to an immunity problem. Without even knowing it, if you present with one or more of these symptoms you could have an immune disorder and not realise it. Supporting your immune system to ensure optimal function can change your health, even in the smallest of ways and change the way you think, feel and function daily.
For information on how to support your immune system, follow this link or visit our Nutrition page to see which foods will optimise immune function.
- Address heavy metals and pesticides
- Buy organic
- Clean up your diet
- Make healthier lifestyle choices by avoiding mercury-rich fish and hormone-laden meat.
For more information on heavy metals and pesticides – See: the “You Should Know” page
Many people slowly develop autoimmune conditions like leaky gut syndrome without even realizing anything is wrong. It can take many years before a diagnosis is reached as the average person will visit many doctors trying to resolve their health issues, before the problem is recognised as autoimmunity because the symptoms of these diseases are so vague and disparate.
Common Autoimmune Disease Symptoms
- Headaches
- Anxiety
- Brain fog
- Attention deficit problems
- Body rashes, red bumps on facial skin and red flaking skin
- Acne
- Rosacea
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
- Allergies
- Asthma
- Dry mouth
- Frequent colds
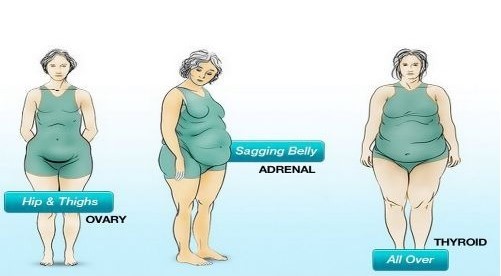
- Thyroid issues – Hashimoto’s disease (underactive thyroid) or Graves disease (overactive thyroid)
- Fatigue or hyperactivity
- Weight gain or loss
- General feeling of malaise
- Anxiety
- Muscle pain and weakness
- Stiffness and pain (could suggest rheumatoid arthritis or fibromyalgia symptoms)
- Feeling “wired and tired”
- Exhaustion
- Digestive tract upset may indicate irritable bowel disease
- Stomach cramping
- Gas
- Bloated stomach
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
If you do have any of these symptoms, please don’t ignore them, hoping they’re nothing serious or that they’ll just go away on their own.
Gut Flora and Autoimmunity
Scientists are focusing on gut flora as a means of treating autoimmune diseases. Read more here.
Conventional Treatments
- Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- immunosuppressants are often used.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin may also occasionally be used.
Natural Treatments